Comparison of guided insertion of the LMA ProSeal™ vs the i-gel™
Authors
Gasteiger L. et al.
Publication
Anaesthesia 2010; 65 (9): 913-916.
Summary
- A study to compare the performances of the LMA ProSeal™ and the i-gel™ supraglottic airway devices in anaesthetised female patients undergoing elective gynaecological or orthopaedic surgery in the supine position
- The LMA ProSeal™ and the i-gel™ supraglottic airway devices were associated with similarly high insertion rates when a duodenal tube-guided insertion technique was employed
- The LMA ProSeal™ formed a more effective seal for ventilation than the i-gel™
Objectives:
- To compare the performances of the LMA ProSeal™ and the i-gel™ supraglottic airway devices in anaesthetised female patients undergoing elective gynaecological or orthopaedic surgery in the supine position
Method:
- This was a prospective trial conducted in American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status 1-2 patients aged 19-70 years with normal airways
- Patients were randomised to receive the LMA ProSeal™ or the i-gel™ device for airway management
- Variables of interest were (i) ease of insertion using a duodenal tube-guided insertion technique and (ii) oropharyngeal leak pressure
Results:
- Patients (mean age 40-41 years, mean body weight 65 kg) were randomly assigned to receive either the LMA ProSeal™ (n=76) or the i-gel™ (n=76)
- One patient who received the i-gel™ was excluded from the analysis after bile-stained fluid was observed in the airway tube post-insertion (the patient’s trachea was intubated and aspiration did not occur)
- Both devices were successfully inserted within two attempts
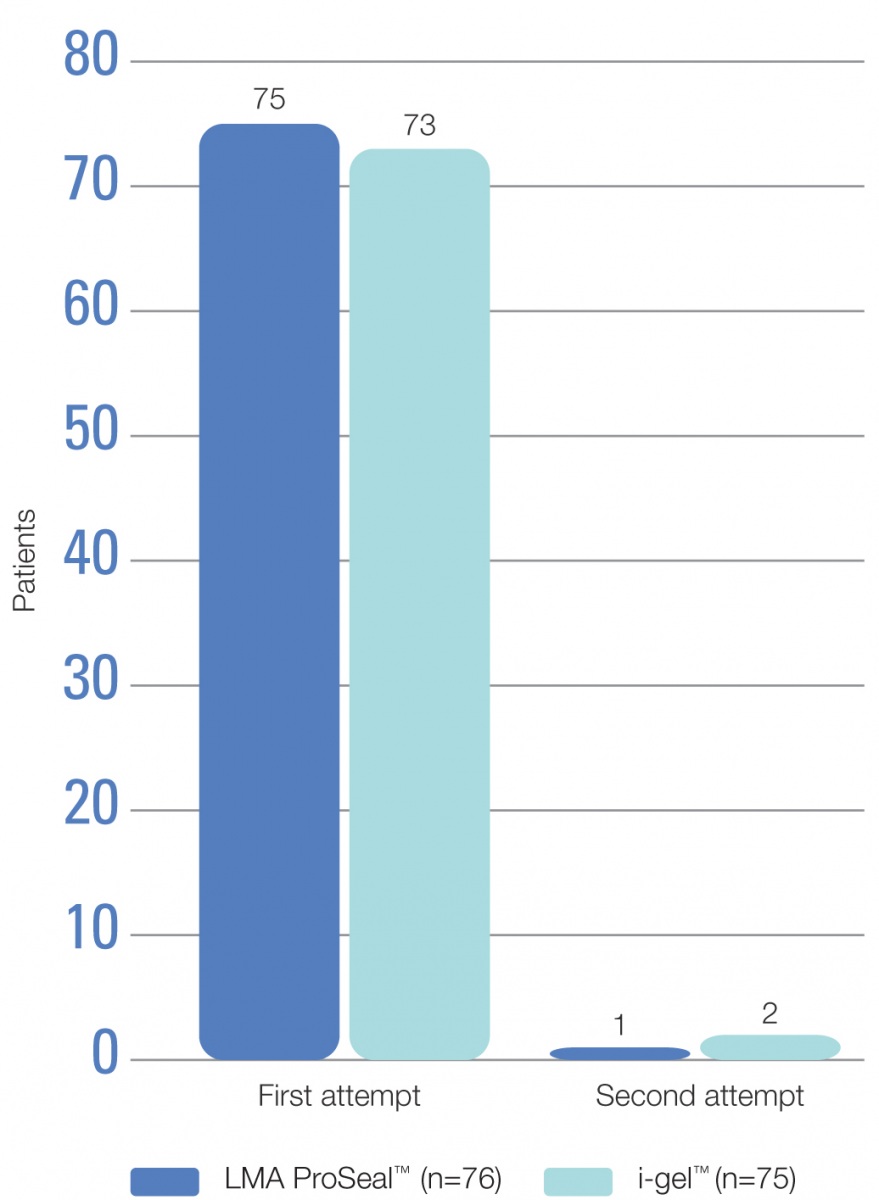
- The rate of success on the first attempt was high in recipients of both the LMA ProSeal™ and the i-gel™ (Figure 1)
- In both groups of patients, the reason for an unsuccessful insertion on the first attempt was an inability to pass the duodenal tube into the oesophagus
Figure 1. Success rate on the first and second insertion attempt with the LMA ProSeal™ and i-gel™ devices using a duodenal tube-guided insertion technique
- The mean time to insertion was 40 seconds in LMA ProSeal™ recipients and 43 seconds in i-gel™ recipients
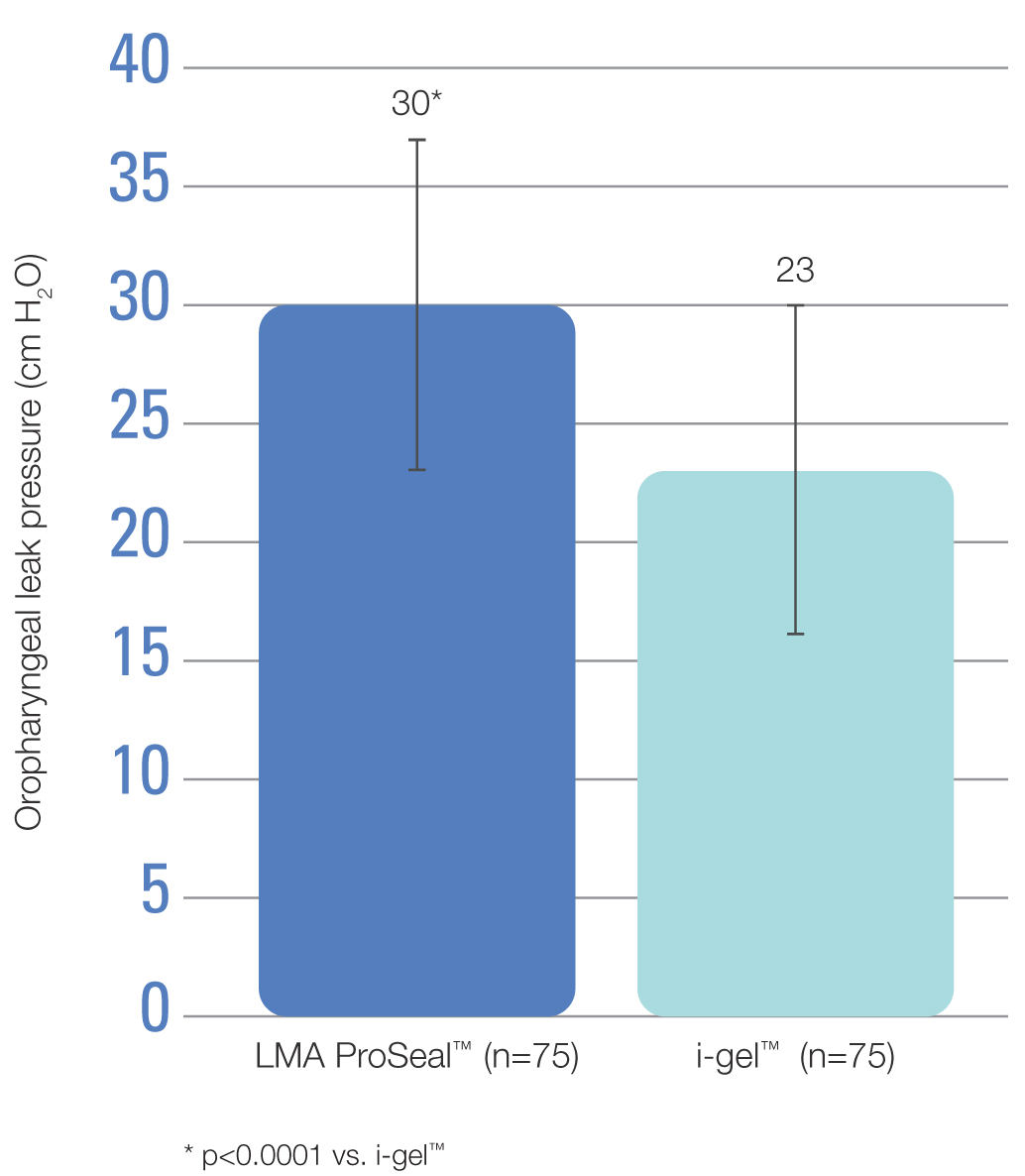
- Mean oropharyngeal leak pressure was significantly (p<0.0001) higher in patients who received the LMA ProSeal™ versus the i-gel™ (Figure 2)
- An oropharyngeal leak pressure of >40 cm H2O was observed in 14 and 6 patients who received the LMA ProSeal™ and i-gel™, respectively
- No adverse events were reported during the course of the study
Figure 2. Oropharyngeal leak pressure with the LMA ProSeal™ and i-gel™ devices (data are shown as mean ± standard deviation)
Conclusions:
- The use of a duodenal tube-guided insertion technique resulted in similarly high insertion rates with the LMA ProSeal™ and the i-gel™ supraglottic airway devices
- The LMA ProSeal™ formed a more effective seal for ventilation than the i-gel™, as demonstrated by significantly higher oropharyngeal leak pressure